The Business Case for Synthetic Data: Real-World Use Cases Driving Enterprise AI Success
For medium to large enterprises, the journey to operationalizing AI is constantly hampered by data privacy, data scarcity, and data quality. Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA ,synthetic data offers a competitive edge for privacy-proof innovation. Organizations that move decisively to build synthetic data capabilities position themselves to accelerate AI initiatives, navigate increasingly complex regulatory environments, and capitalize on data-driven opportunities that remain inaccessible to competitors constrained by traditional data approaches.
This is where Synthetic Data, artificially generated data that mathematically and statistically mirrors real-world data, emerges as a strategic game-changer.
For high-level decision-makers and C-suite professionals, synthetic data represents a powerful business solution that de-risks, accelerates, and scales the entire enterprise AI roadmap. It's the key to achieving unprecedented levels of security, speed, and innovation without compromising customer trust or regulatory standing.
What Is Synthetic Data And Why Does It Matter For Enterprises?
Simply put, synthetic data is data created by algorithms rather than generated by real-world events. Crucially, it retains the statistical properties, relationships, and variance of the original data, making it functionally equivalent for training AI and machine learning models.
For enterprise leaders, the value proposition is rooted in strategic risk mitigation and competitive advantage:
- Zero-Risk Privacy Compliance: Because synthetic data contains no direct mappings to individual real-world entities, it is inherently anonymized. This allows teams to innovate freely and share data across borders or departments without the fear of massive regulatory fines or data breaches.
- Scaling AI Development: Synthetic data can be generated on-demand, in massive quantities, overcoming the limitations of real-world data collection, especially for rare events or scenarios (e.g., fraud types, autonomous driving corner cases).
- Unlocking Latent Value: It enables the use of sensitive internal data for external partnerships, allowing for collaborative AI development while strictly maintaining internal data security.
The strategic decision to invest in synthetic data is a decision to de-risk innovation and accelerate time-to-market for AI-powered products and services.
Addressing Critical AI Challenges & Enhancing Data Utility
Synthetic data directly addresses the core inhibitors of AI adoption within large organizations:
AI Challenges Synthetic Data Fixes
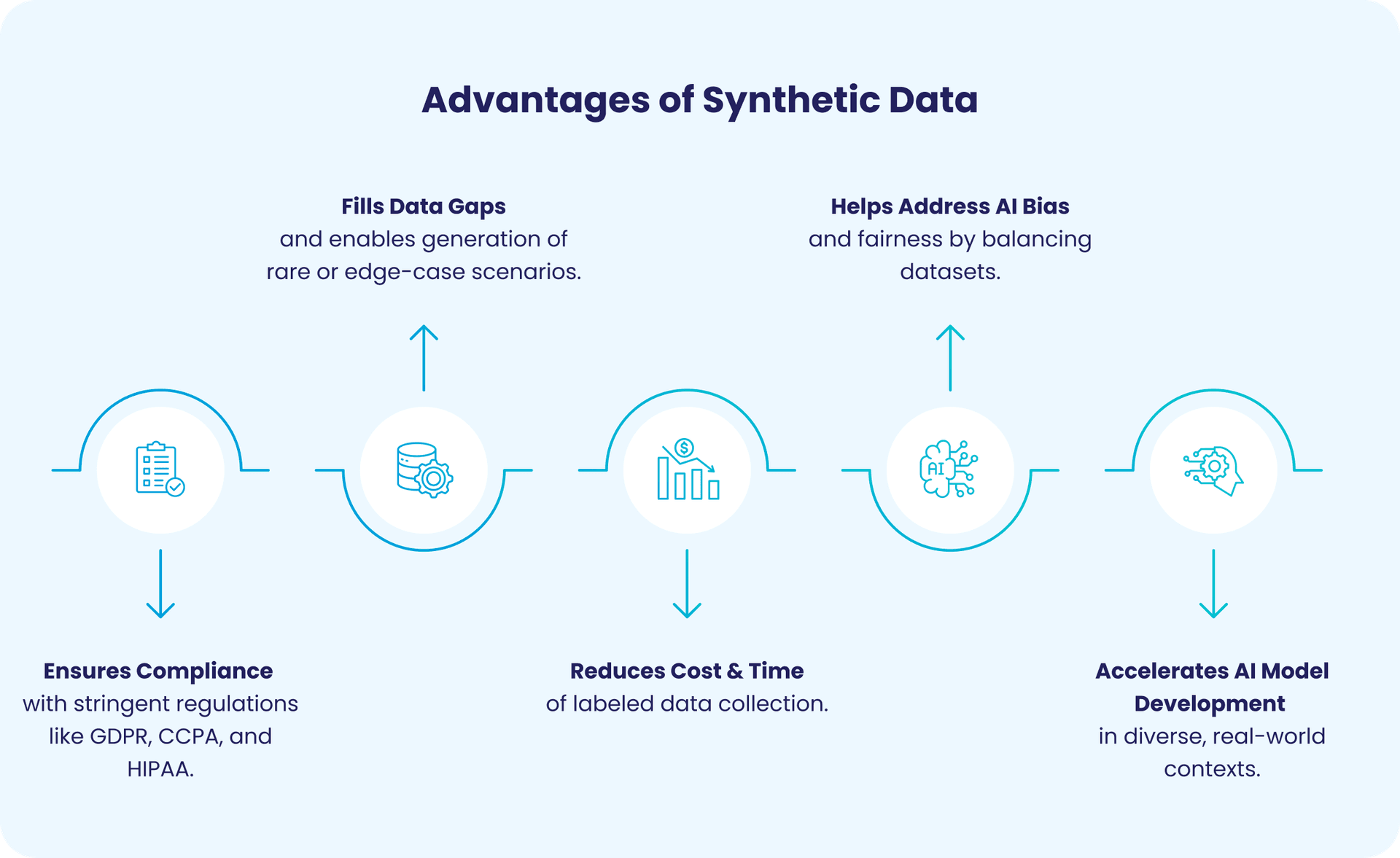
- Data Scarcity: Real-world data for rare events (e.g., fraud detection, medical anomalies) is often limited. Synthetic data fills these gaps, enabling robust model training and better performance in edge cases.
- Privacy & Compliance Concerns: Sharing sensitive data can violate regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. Synthetic data mimics real patterns without exposing personal information, ensuring privacy compliance and reducing legal risks.Traditional anonymization methods often fail to fully protect data or destroy the statistical utility required for effective model training; synthetic data bypasses this trade-off.
- Bias Reduction: Imbalanced datasets lead to skewed AI outcomes. Synthetic data helps create balanced, representative samples by generating data points for underrepresented groups, improving fairness and model accuracy in predictions across all customer segments.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Collecting and labeling large datasets is resource-intensive. Generating synthetic data is often orders of magnitude cheaper and faster, accelerating development cycles and cutting costs while maintaining data quality.
Compliance Deep Dive: The Regulatory Shield
Data governance is paramount in today’s global regulatory landscape. Synthetic data provides a vital shield by:
- Protecting PHI (Healthcare): Generating synthetic patient data allows researchers to train diagnostic AI models on realistic populations without ever exposing actual patient PII or PHI, dramatically speeding up medical advancements.
- Enabling Global Transfer (GDPR): Synthetic customer data, generated locally and then transferred, eliminates the regulatory burden of crossing jurisdictional lines between regions with different privacy laws, enabling a truly global AI strategy.
What Are The Real-World Business Cases For Adopting Synthetic Data?
The theoretical benefits are now translating into tangible, high-value outcomes across multiple industries. Here's how forward-thinking companies are deploying synthetic data to drive measurable results:
1. Financial Services: Superior Fraud Detection
- The Challenge: Detecting rare but high-impact fraud requires vast amounts of transactional data, but real fraud data is scarce and highly sensitive. Training models on limited real data leads to poor generalization and high false-positive rates.
- The Solution: Banks use generative adversarial networks (GANs) and variational autoencoders (VAEs) to create synthetic transaction data that includes statistically accurate, yet completely artificial, rare fraud patterns. This allows models to be trained on millions of examples of fraud that have never occurred in reality, leading to a significant increase in detection accuracy and a reduction in customer inconvenience from false alarms.
2. Autonomous Systems: Overcoming the "Corner Case" Problem
- The Challenge: Self-driving vehicles and robotic systems must be tested rigorously against millions of miles of driving data, particularly for dangerous or rare corner case scenarios (e.g., a specific weather condition combined with a specific object placement). Waiting for these events to happen in the real world is impractical and unsafe.
- The Solution: Synthetic data platforms generate hyper-realistic visual and sensor data (including lidar and radar) for these corner cases via physics-based simulations. This massive, on-demand supply of critical training data allows autonomous systems to be safely and rapidly tested in a virtual environment, cutting development timelines and increasing safety performance to a level unattainable with physical testing alone.
3. Retail & E-commerce: Optimizing Supply Chains
- The Challenge: Retailers need to simulate complex supply chain disruptions (e.g., port closures, sudden demand spikes) to stress-test their logistics models, but historical data for truly novel disruptions is, by definition, unavailable.
- The Solution: Synthetic data models can generate millions of simulated demand, inventory, and logistics datasets under hypothetical stress conditions. This enables the optimization of inventory placement, staffing, and distribution networks, leading to a measurable reduction in operational expenditure and improved customer satisfaction through better fulfillment.
Strategic Case Studies
Companies across sensitive, data-intensive industries are leveraging synthetic data to solve specific, high-stakes problems:
| Company & Industry | Challenge Addressed | Synthetic Data Solution | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIX (Financial Services) | Training AI for fraud detection Without exposing sensitive customer data; real data scarcity stalled innovation | Generated anonymized transaction datasets mimicking real patterns, complete with rare fraud signals. | ML models Improved accuracy by 35% reducing false positives and operational losses by €2.5 million annually |
| Mayo Clinic (Healthcare) | Training diagnostic AI Without patient consent hurdles; need diverse datasets covering rare diseases | Simulated electronic health records (EHRs) with GANs to create diverse, privacy-safe populations. | Models trained on synthetic EHRs in predicting readmissions, on par with real data, with zero privacy risks |
| BMW (Automotive) | Generating diverse driving data Demand for petabytes of data, including hazardous edge cases impractical to collect physically | Generated virtual road scenarios via physics-based simulations (crashes, adverse weather, pedestrian behaviors). | Cut training time and enhanced Computer Vision models' edge-case handling |
| Walmart (Retail) | Demand forecasting Volatile demand across thousands of SKUs causing stockouts and overstock issues | Implemented AI algorithms leveraging historical sales, search trends, weather, and events to forecast demand at a granular level. These models were stress-tested using synthetic scenarios to optimize inventory allocation. | Reduced stockouts by 30% and excess inventory by 20–25%, improving customer experience and cutting operational costs |
What Is The ROI Of Synthetic Data?
Synthetic data shifts the paradigm from data scarcity to data abundance, fundamentally changing the speed and scope of what an enterprise can achieve with AI.
- Accelerated Model Training: Instead of waiting months for sufficient labeled data, development teams can spin up synthetic datasets in hours or days. This dramatically shrinks the AI development lifecycle, allowing companies to launch new predictive models at a velocity that outpaces competitors.
- Rapid Prototyping & Sandboxing: Data science teams can prototype solutions using synthetic data without needing access to sensitive production environments. This "sandbox" approach allows for faster experimentation and iteration.
- Compliance Cost Avoidance: The robust protection offered by synthetic data acts as an insurance policy against the catastrophic costs of a major data breach or GDPR fine.
- Speed-to-Market Advantage: By accelerating the AI development lifecycle from months to weeks, synthetic data allows enterprises to be first-to-market with innovative products (e.g., new credit scoring models), capturing market share and increasing revenue streams ahead of the competition.
How Should Organizations Implement Synthetic Data Strategically?
Initial synthetic data implementations can begin with relatively modest infrastructure using cloud-based generation platforms. As programs mature, organizations typically invest in specialized generation infrastructure, establish dedicated synthetic data engineering capabilities, and align with MLOps practices for scalability.
Emerging Trends Shaping The Future
- Generative AI Refinement: Advances in LLMs and diffusion models improve correlation capture and data fidelity, enhancing realism for complex synthetic datasets. Studies show these techniques can boost downstream task performance by up to 7%, indicating significant gains in quality.
- Real-Time Synthesis: Future architectures may synthesize data on-demand as operational applications require it, maintaining continuous statistical alignment with production data.
- Cross-Organizational Collaboration: Banks are forming agreements to safely share synthetic data across borders, enabling collaborative AI development without violating local privacy compliance laws.
- Democratization of Tools: New tools are simplifying the process to check synthetic data for privacy and model accuracy, accelerating adoption beyond organizations with deep AI expertise.
- Regulatory Maturation: Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize synthetic data, reducing adoption risk and establishing it as an accepted component of data governance architectures.
Conclusion: Transforming Data Constraints into Competitive Advantages
Organizations implementing strategic synthetic data programs achieve faster innovation cycles, reduce operational costs, improve AI model performance, and unlock collaboration opportunities previously constrained by data sharing limitations. As we progress, synthetic data will transition from competitive differentiator to table stakes capability for data-driven enterprises.
with 85% of AI projects failing due to data issues, synthetic data offers a competitive edge for privacy-proof innovation. Organizations that move decisively to build synthetic data capabilities position themselves to accelerate AI initiatives, navigate increasingly complex regulatory environments, and capitalize on data-driven opportunities that remain inaccessible to competitors constrained by traditional data approaches.
Ready to Transform Your AI Journey with Sythentic Data?
Consult with our specialists to assess your data readiness, identify key data opportunities and get a custom roadmap for your enterprise success.
FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions
Table of Contents
Newsletter Signup
Tomorrow's Tech & Leadership Insights in
Your Inbox
Discover New Ideas

The Future of Healthcare Portals: How AI Agents are Transforming Patient Engagement

Modernizing Manufacturing: Using Computer Vision for Real-Time Quality Control

3+ Applications of Big Data in Healthcare (Real Examples)

Knowledge Hub

